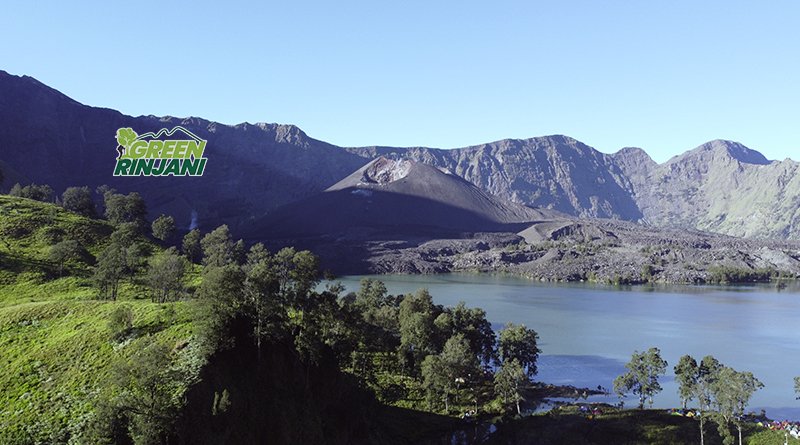
Mount Rinjani is one of Indonesia’s most spectacular volcanoes and a world-class trekking destination located on Lombok Island, West Nusa Tenggara. Rising to 3,726 meters above sea level, Mount Rinjani is the second-highest volcano in Indonesia and the most iconic mountain on Lombok.
Internationally, Rinjani mountain has been recognized as one of the best trekking destinations in the world, earning global attention through travel authorities such as Lonely Planet, which highlights Rinjani for its dramatic landscapes, challenging trails, and unique volcanic scenery. Its combination of summit climbs, crater rim hikes, and lake expeditions places Mount Rinjani among the most rewarding multi-day treks in Southeast Asia.
What makes Mount Rinjani truly exceptional is its diversity. Trekkers encounter open savannah hills, dense tropical rainforest, volcanic ridges, and the vast Segara Anak crater lake, with the active Mount Barujari volcanic cone rising from its center. Beyond adventure, Mount Rinjani also holds deep cultural and spiritual importance for local Sasak communities, making it both a natural wonder and a sacred landscape.
As a protected national park, Mount Rinjani is not simply a trekking destination, but a regulated conservation area where access, routes, and activities are carefully managed to preserve its fragile ecosystem for future generations.

Where Is Mount Rinjani Located?
Mount Rinjani is located in North Lombok, within the administrative boundary of
Rinjani National Park (Taman Nasional Gunung Rinjani – TNGR).
Geographic Overview of Gunung Rinjani
- Island: Lombok, Indonesia
- Province: West Nusa Tenggara (NTB)
- Elevation: 3,726 meters above sea level
- Coordinates: Approx. 8°25′ South, 116°27′ East
- Landscape: Volcano, caldera, crater lake, savannah, rainforest
Rinjani Mountain dominates Lombok’s northern skyline and can be seen from many parts of the island
on clear days, including coastal regions.
Rinjani Zero Waste & Trekking Regulations
To protect its fragile ecosystem, Mount Rinjani National Park actively enforces strict environmental policies, including the official Rinjani Zero Waste Program. Through this program, the park management ensures that every trekker and trekking operator takes responsibility for waste management while trekking on Mount Rinjani.
As part of the Zero Waste regulation, trekkers must follow several mandatory rules, including:
- Carry all personal trash back out of the national park
- Avoid bringing single-use plastic items
- Undergo waste checks before entering and after exiting the trail
- Participate in waste deposit or accountability systems when required
In addition, these environmental rules form part of Rinjani’s broader Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). These SOPs also regulate trekking safety standards, official route usage, daily visitor quotas, and licensed guide requirements.
By following these regulations, visitors help preserve Rinjani as a sustainable trekking destination. At the same time, compliance supports conservation efforts and ensures that future generations can continue to experience Gunung Rinjani in its natural state.

Mount Rinjani Entrance Ticket & Permit Overview
Access to Mount Rinjani is regulated through the Mount Rinjani National Park permit system, which applies to all trekkers without exception.
General Ticket & Permit Information:
- National Park entrance fee: IDR 250,000 per person per day
- Permit system: Mandatory registration via official TNGR channels
- Quota system: Daily limits apply for each trekking route
- Additional requirements: Licensed guide, registered trekking route, and compliance with park regulations
The total cost of trekking Rinjani may vary depending on trek duration, route, and services included. For this reason, detailed pricing and package breakdowns are explained separately on dedicated pages.
👉 For complete and up-to-date price details, please refer to the Mount Rinjani trekking price guide available via the sidebar.
Rinjani National Park (TNGR)
Mount Rinjani National Park was officially established in 1997 to protect the mountain’s ecosystems, manage trekking activities, and preserve its cultural value.
The park covers approximately 41,330 hectares, consisting of:
- Tropical rainforest
- Highland savannah
- Subalpine and alpine zones
- Rivers, waterfalls, and volcanic features
All trekking activities on Mount Rinjani must comply with TNGR regulations, including:
- Mandatory trekking permits
- Daily visitor quotas
- Official route usage
- Waste management and zero-waste policies
Mount Rinjani is not an open-access mountain. Entry is strictly controlled to protect both nature and visitors.
How to Access Gunung Rinjani
There is no direct road access to Mount Rinjani itself. All visitors must enter through official trekking gateways designated by Mount Rinjani National Park.
Common Access Points to Rinjani:
- Lombok International Airport (BIL): 3–5 hours by car
- Mataram / Senggigi: 3–4 hours
- Kuta Lombok: 4–5 hours
Every trek on Mount Rinjani must:
- Start from an official gateway village
- Be registered in the TNGR permit system
- Follow approved routes only
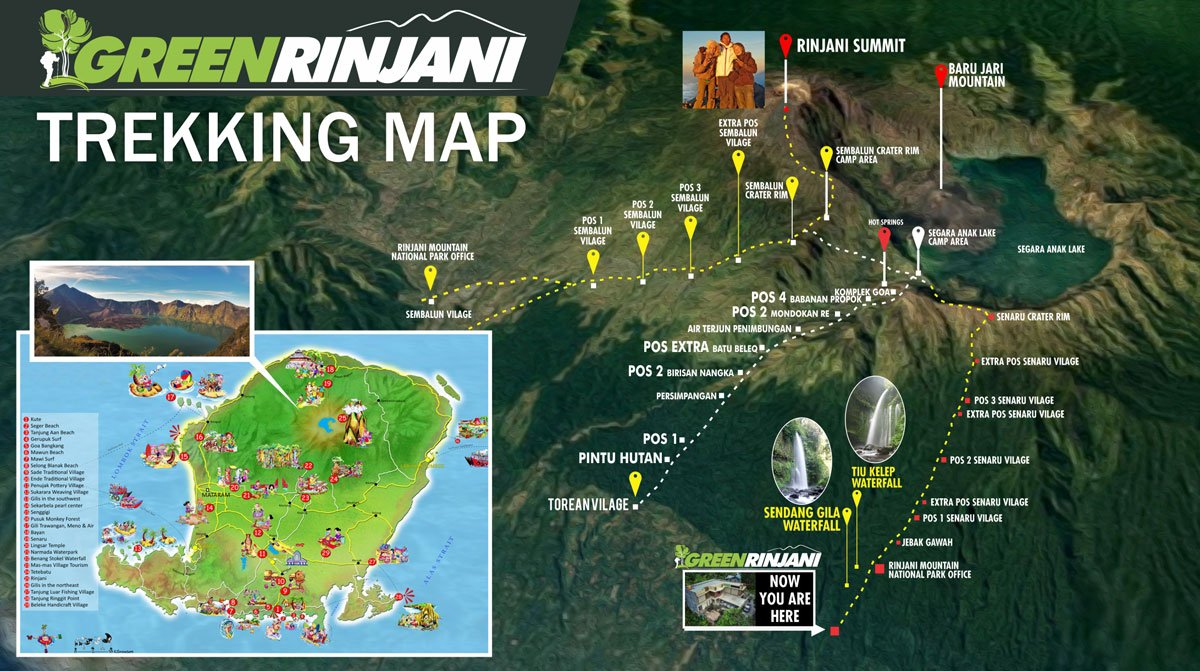
Official Trekking Routes of Rinjani Mountain
Mount Rinjani National Park officially recognizes four trekking routes. Only these routes are legally open for trekking.
Sembalun Route – Rinjani Summit Route
The Sembalun Route is the primary route used to reach the Mount Rinjani summit.
Route details:
- Start point: Sembalun Village (1,156 m)
- Destination: Summit (3,726 m) and Sembalun Crater Rim
- Terrain: Open savannah, rolling hills, volcanic sand
- Notable section: Seven Hills (Tujuh Bukit)
Seasonal status:
- Open: April – December
- Closed: January – March
Senaru Route – Forest & Crater Rim Route
The Senaru Route passes through dense tropical rainforest and leads to the Senaru Crater Rim.
Route details:
- Start point: Senaru Village (601 m)
- Destination: Senaru Crater Rim
- Terrain: Forest trail, stone steps, shaded paths
- Highlights: Rainforest ecosystem, panoramic lake views
This route is ideal for crater rim trekking and longer summit combinations.
Torean Route – Scenic Valley Route
The Torean Route is considered the most scenic route on Mount Rinjani and is mainly used as a descent route.
Route details:
- Exit point: Torean Village
- Terrain: River valleys, waterfalls, rocky paths
- Highlights: Segara Anak Lake, hot springs, dramatic cliffs
Important notes:
- Rarely used as an ascent route
- Requires good balance and stamina
- Open conditionally, depending on weather and trail safety
Tetebatu Route – South Mount Rinjani Eco Trek
The Tetebatu Route is located on the southern slope of Rinjani Rinjani and focuses on eco-tourism and cultural trekking.
Route details:
- Start point: Tetebatu Village
- Terrain: Rice terraces, bamboo forest, waterfalls
- Elevation: Low to mid-altitude only
This route does not reach the summit or crater lake and is designed for light trekking experiences.
Routes That Are Not Officially Open
Any route outside the four official routes above is not permitted.
Trekkers are not allowed to:
- Create new trails
- Enter mountain Rinjani without registration
- Trek without licensed guides
- Camp outside designated zones
Illegal trekking on Mount Rinjani poses serious safety risks and causes long-term environmental damage.
Gateway Villages Around Mount Rinjani
Several traditional villages serve as official gateways to Mount Rinjani:
- Senaru Village – Northern gateway, forest routes, waterfalls
- Sembalun Village – Eastern gateway, summit access
- Tetebatu Village – Southern eco-tourism gateway
- Torean Village – Valley exit route
Most licensed guides and porters come from these villages and depend on sustainable Mount Rinjani trekking for their livelihoods.
Trekking Season and Route Closures on Mountain Rinjani
Mount Rinjani National Park applies strict seasonal control:
- Open season: April – December
- Closed season: January – March
Temporary closures may also occur due to:
- Heavy rainfall
- Landslides
- Volcanic activity
- Trail damage
Always check the latest official Mount Rinjani status before planning a trek.

Why Understanding Route Information Matters
Mount Rinjani is not an open-access mountain. It is a protected national park with ecological, cultural, and safety considerations.
Understanding:
- Where Rinjani mountain is located
- Which routes are officially open
- How access and permits work
is essential for safe, legal, and responsible trekking.
Respecting these systems helps protect Rinjani Moutain for future generations and ensures that local communities continue to benefit from sustainable tourism.

